Laser Treatment In Urology
Prostate laser surgery is used to relieve moderate to severe urinary symptoms caused by an enlarged prostate, a condition known as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
All lasers use concentrated light to generate precise and intense heat. Prostrate Laser surgery removes excess prostate tissue by:
Ablation. The laser melts away excess tissue. Example: KTP Greenlight laser
Enucleation. The laser cuts away excess prostate tissue. Example: HoLEP
There are different types of prostate laser surgery, such as:
Photo selective vaporization of the prostate (PVP). A laser is used to melt away (vaporize) excess prostate tissue to enlarge the urinary channel.
Holmium laser ablation of the prostate (HoLAP). This is a similar procedure to PVP, except that a different type of laser is used to melt away (vaporize) the excess prostate tissue.
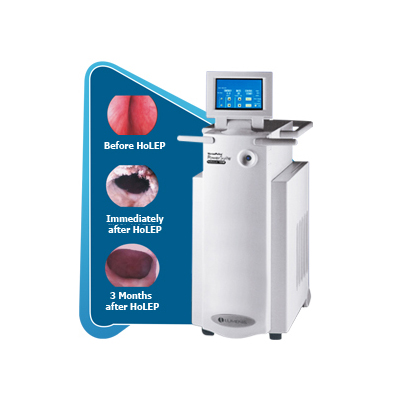
Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate (HoLEP). The laser is used to cut and remove the excess tissue that is blocking the urethra. Another instrument, called a morcellator, is then used to chop the prostate tissue into small pieces that are easily removed.
Book Your Appointment
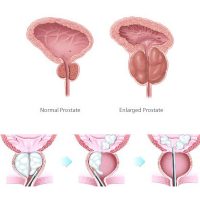
Prostate (HoLEP)
Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate (HoLEP) is a minimally invasive treatment for BPH. The surgeon uses the laser to enucleate the prostate gland tissue, leaving just the capsule in place. HoLEP is performed transurethrally, using a holmium laser to separate the plane between the prostate gland tissue and the prostate capsule. This prostate laser surgery allows complete resection of all adenomatous tissue, minimizing the need for future re-treatment.
HoLEP offers some distinct advantages:

